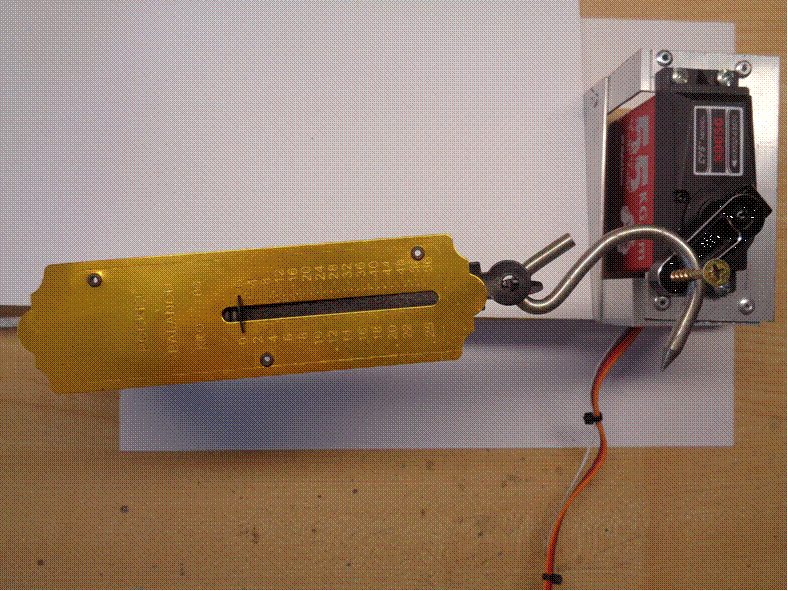
In this test the servo is producing
17Kg of torque at 3 cm. The pivot point to the load measuring
point is 3 cm.



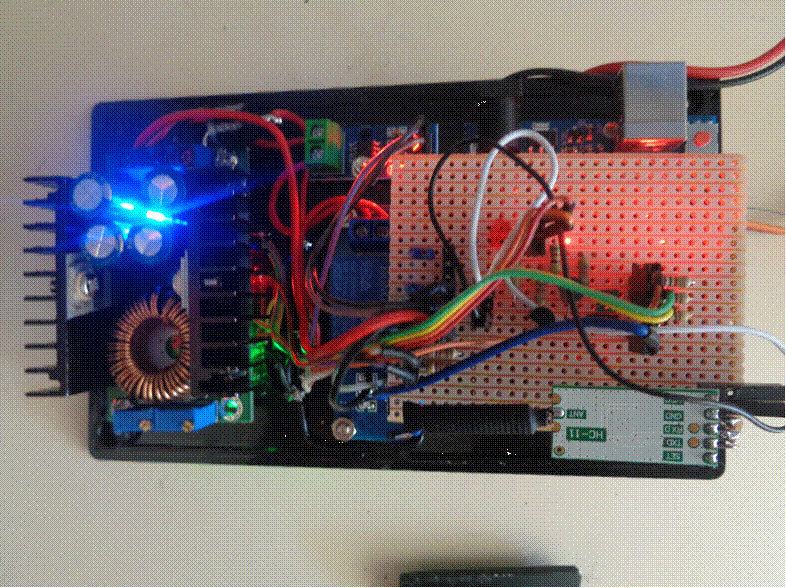
Power supply - Power relay - Current
detector - Servo control - Wireless communications modem
Control unit
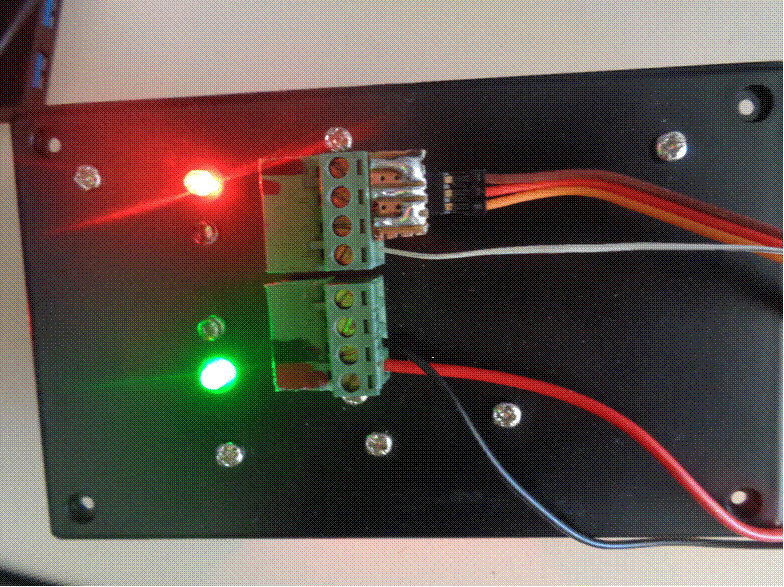
Connection terminals and external signal and road
direction indicators.
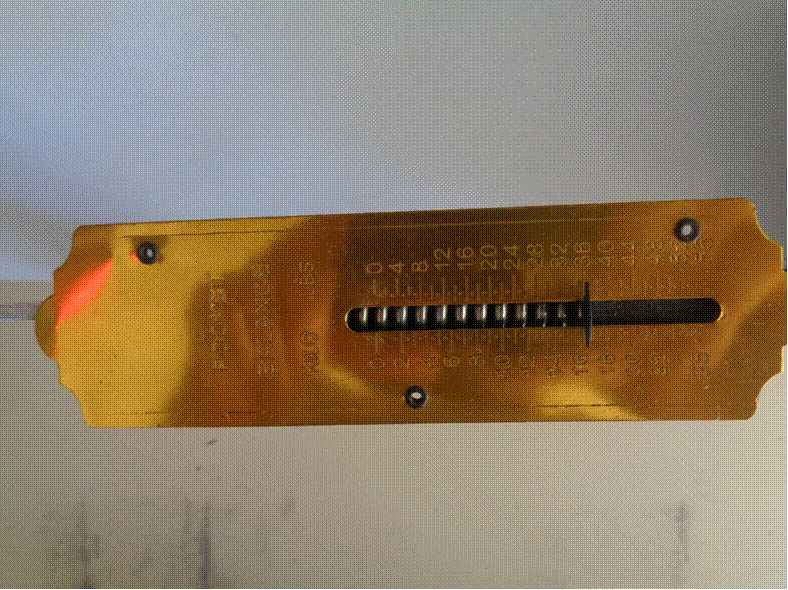
Servo internal potentiometer showing external
connection.
![]()
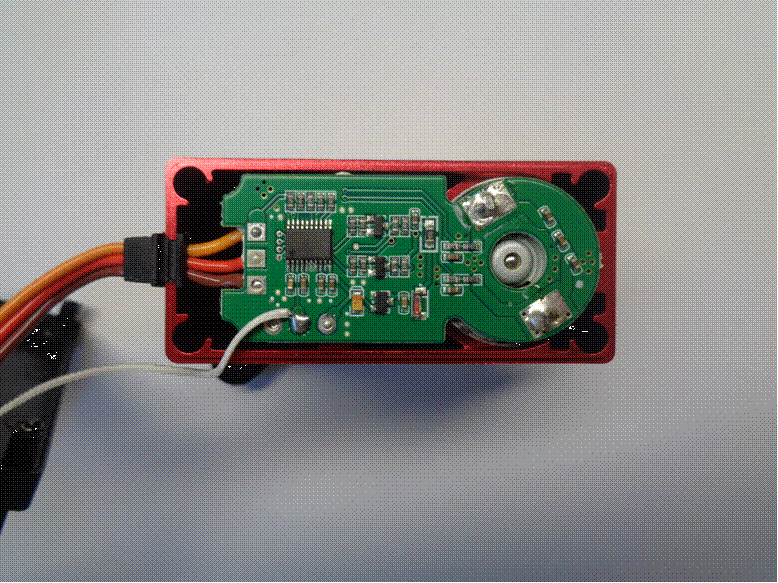
White wire connected to the potentiometer wiper.
![]()
Hole drilled in the servo top plate allowing the white
wire to exit.
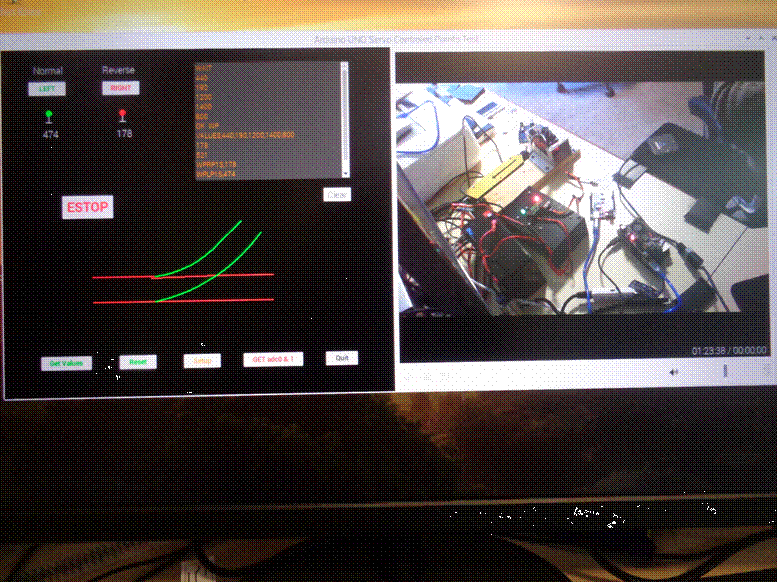
Servo test software points in normal position.
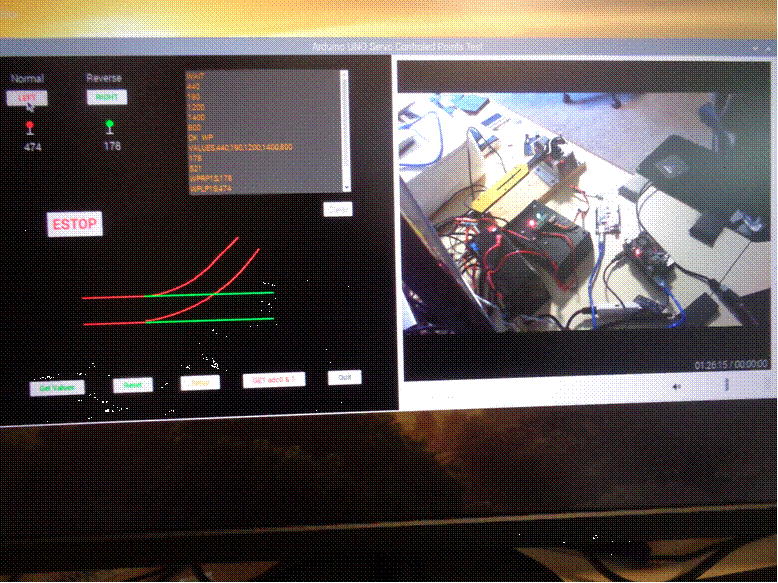
Servo test points in reverse position.
Servo
test
software setup page.
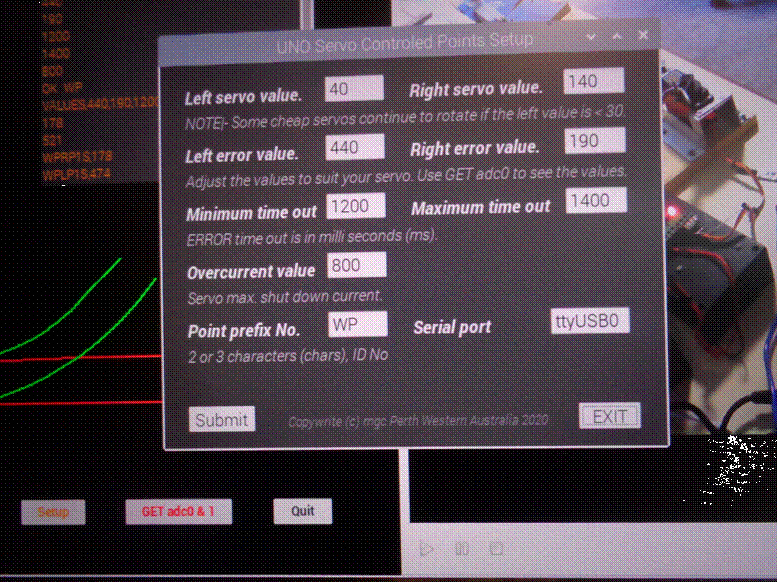
![]()
The PC or Raspberry Pi control
program was cut using Gambas3. For more info see the Gambas
page.
The test system has position,
current (Amps.) and time out protection to avoid failed, split
or damaged points from
being operated along with visual indication by the LED’s
displaying DANGER red on failures. The use of current
detection and position sensing is a great advance in over
coming point failures. One of the downfalls of most
railways point safe working. That is being able to detect
stones, rocks and other debris jamming or splitting the
points causing derailments. Adding video surveillance
to individual points would also be of great assistance
in safe working. The greatest advantage in using a servo motor
is it can be programmed to go to any position
within its 180 deg. Sweep (this 55Kg servo has a 0 to 180 deg
sweep). The numbers displayed in the setup
page represent the actual 12 bit analog
values used to control the servo position. The ability to
change the
stop and start positions of the servo by software makes it a
simple operation to correct for point wear and tear
and any other unforeseen deviations.